Hungary has great traditions in industry. The main fields are mechanical engineering and the processing industry. In recent years, numerous international companies have set up production sites in Hungary, followed by various suppliers. In the services sector, tourism, financial and software services are the most important. Companies such as Vodafone and IBM have established Shared Service Centers in Hungary.Hungary has very attractive conditions and is one of the most favorable investment countries in Central and Eastern Europe.This statement was confirmed by numerous, positive facts:
The best infrastructure in the region (Central Europe) with approximately 2 000 kilometers of motorway and highways;
More than 200 commercial parks with excellent infrastructure;
Several hundred thousands of well-motivated and above-average skilled workers with the most diverse qualifications and experiences (from assistants to several foreign-language engineers)
A 9% tax rate and a flat tax rate of 15% are among the most attractive tax rates in Europe, both for companies and for individuals.
Hungary has been chosen as an investment location by renowned companies from the German-speaking countries in recent years. From Daimler-Benz, Audi, BMW, Bosch, Wienerberger, Nestlé or Stadler Rail (major manufacturer of rapid-transit railway), with which numerous suppliers have settled.
Hungary in Numbers
- Area: 93 030 km2
- Capital: Budapest
- Official language: Hungarian
- Languages of business communication: Hungarian, English, German
- EU-Membership: since 2004
- GDP 2018: USD 157 861 million
- Currency: Hungarian forint (Ft, HUF)
- Government type: Republic
- Population: 9,730,000 people
- Road network: total 32 000 km; motorways: 1883 km
Economic data
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in Hungary
Change in GDP Volumes
(compared to same quarter, previous year)
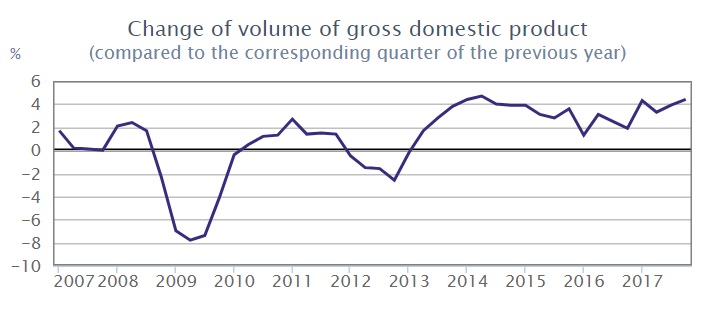
Source: Hungarian Central Statistical Office (KSH)
Foreign Direct Investments (FDI)
In the successful restructuring of the Hungarian economy since 1990, foreign direct investment was of crucial importance. The continuous inflow of foreign direct investment contributed and contributed decisively to the increase in productivity, technological modernization, the expansion of export capacities necessary for a healthy growth structure and the creation of new jobs.
Most investments were made in the service sector as well as in the competitive industries of the manufacturing industry (production of cars, production of PCs, electronic and optical products).
78.6% of direct investment in Hungary came from the European Union, of which 26.4% came from Germany. Most investments were made in the service sector as well as in the competitive industries of the manufacturing industry (production of cars, production of PCs, electronic and optical products).
Over the past few years, the automotive industry has seen a surge in direct investment. The Daimler Group opened its new, most modern factory in Kecskemét in 2012 and the two car manufacturers Audi (in Győr) and Opel (in Szentgotthárd), which were already established in Hungary, expanded their production capacities. In 2019, BMW starts building its new factory in Debrecen, which will offer more than 1 000 new workplaces in Eastern- Hungary. These developments led to an increase in the number of car suppliers.
The chemical companies supplying the automotive industry also recorded significant developments. One of the largest is the new BorsodChem plant worth € 200 million in Kazincbarcika, or the expansion of the South Korean tire manufacturer Hankook in Rácalmás.
A rapidly developing industrial sector is renewable energy sources. In particular, thermal sources of energy and photovoltaic solar collectors have seen significant developments in recent years.
Inflation
In 2019, consumer prices rose by 3.4% on average compared to the previous year. Overall, low inflation and the reduction in household burdens can lead to an increase in disposable income, which together with the high employment rate could stimulate private consumption.
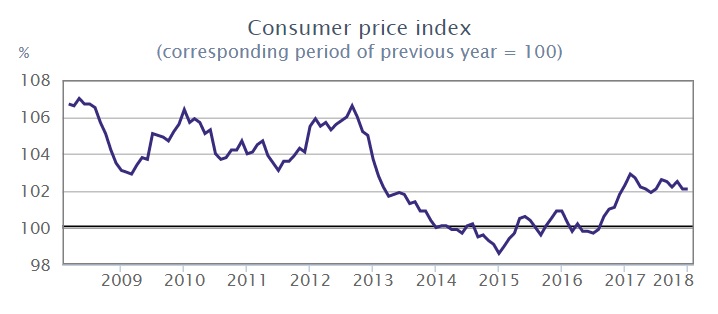
Source: KSH
Labour Market Overview
There was a continuous decrease in unemployment in 2019. The employment rate among the population aged 20–64 was 67.6% in 2019, 0.8 percentage points higher than in the previous year. In terms of unemployment, Hungary is at the top of the European Union. Compared to the 10.2% rate in 2013, the unemployment rate in 2019 has declined to 3.4%, which represents a significant advance. According to a study by the European Commission, this ratio will continue to improve over the next years.
From 2019, the government increased the minimum wage to HUF 161,000 (about 473 EUR) per month and the minimum wage for work areas requiring professional qualification to 210,600 HUF (about 620 EUR) per month. For part-time employees, the agreed monthly, weekly and daily wage is calculated in relation to working time.
The employment indices in Hungary differ greatly from region to region. This is also reflected in the average salaries. Hungary is strongly centralized. Employment and average wages are highest in the central region, ie in Budapest and its surroundings. Thanks to the continuous development of the infrastructure and the targeted regional subsidies, more and more companies with foreign participation from the capital choose more distant locations as a location
